Integrating Closed Loop Insulin Pumps with Dexcom Technology
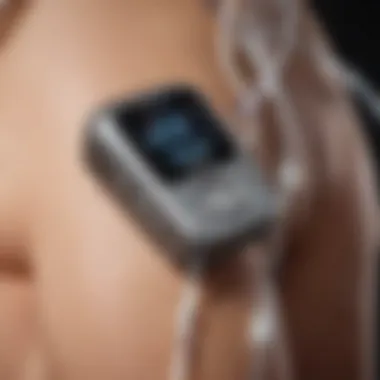

Intro
The management of diabetes has evolved significantly over the years, leading to the introduction of advanced tools that enhance patient care and glucose control. Two key innovations in this domain are closed loop insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems, particularly those developed by Dexcom. This article examines how these technologies interact and improve diabetes management.
The Convergence of Technology
With diabetes, maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is crucial. Closed loop insulin pumps automate insulin delivery based on real-time data, reducing the burden of constant monitoring. Dexcom’s continuous glucose monitors offer accurate, real-time glucose readings, which are critical for effective insulin management. Together, they represent a significant advancement in the realm of diabetes treatment.
The integration of closed loop systems with Dexcom technology highlights how innovation can transform traditional methods of care into a more seamless experience. By automating insulin delivery using precise glucose data, patients can achieve better glycemic control while experiencing enhanced quality of life.
This article will detail the benefits and challenges associated with these technologies, investigate user experiences, and explore future insights into diabetes care. By providing a comprehensive understanding of these developments, it aims to inform students, researchers, educators, and professionals in the field.
Prelims to Diabetes Management
Diabetes management is a critical subject for millions of individuals whose lives are affected by this chronic disease. It requires careful consideration and research into the technologies that can improve glycemic control and enhance overall quality of life. As diabetes cases globally rise, understanding effective management strategies becomes essential not only for patients but also for healthcare providers and researchers.
In this context, the development of advanced medical devices such as closed loop insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors, specifically from Dexcom, represents a significant leap forward. These systems leverage technology to automate insulin delivery and monitoring, offering patients the ability to manage their condition more effectively. The integration of devices aims to minimize the manual effort involved in diabetes management, thus reducing the burden associated with daily calculations of insulin doses and glucose levels.
Additionally, the collaboration between these technologies allows for near real-time adjustments to insulin delivery, enhancing glycemic control. Individuals using these systems often experience not only better health outcomes but also improved daily life, as the stress of diabetes management can be significantly alleviated.
Understanding how these tools work together serves as a foundation for exploring their potential benefits, challenges, and future implications in diabetes care.
Understanding Diabetes Type and Type
Diabetes is categorized mainly into two types, Type 1 and Type 2, each with distinct characteristics and management approaches. Type 1 diabetes typically arises in childhood or adolescence and is characterized by the autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Patients with Type 1 must rely on external insulin delivery, either through injections or pumps, to control blood glucose levels.
In contrast, Type 2 diabetes develops more gradually and usually occurs in adults, although it is increasingly seen in younger populations. This type involves insulin resistance, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin, and it may also involve a gradual reduction in insulin production. Management often includes lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, along with medications that can help improve insulin sensitivity or stimulate insulin release.
Both types of diabetes demand careful monitoring and management to prevent complications.
The Role of Insulin in Glycemic Control
Insulin plays a central role in the regulation of blood sugar levels. It facilitates the uptake of glucose by the body's cells, converting it into energy. When insulin functions properly, it helps maintain a balance between the amount of glucose in the bloodstream and the energy needs of the body.
In individuals with diabetes, this regulation is disrupted. Without effective insulin action, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia. Over time, high blood sugar levels can lead to severe health complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney issues. Therefore, adequate insulin delivery through individualized treatment plans is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
For patients relying on external insulin through pumps, understanding how insulin acts in the body is important. It enables them to make informed decisions about their treatment plan, factoring in their lifestyle, food intake, and energy expenditure. This holistic approach to managing diabetes maximizes the effectiveness of insulin therapy and contributes to improved health outcomes.
Overview of Insulin Pump Technology
Insulin pump technology is a vital element in diabetes management. It stands at the forefront of revolutionizing the way individuals with diabetes control their blood sugar levels. Insulin pumps provide a continuous supply of insulin, allowing for better glucose management compared to traditional methods. Understanding this technology deepens the insights into its benefits and challenges.
What is an Insulin Pump?
An insulin pump is a medical device designed to deliver insulin continuously throughout the day. Unlike traditional approaches involving multiple daily injections, insulin pumps adjust insulin delivery automatically based on the user’s needs. This method helps maintain a steadier blood sugar level, reducing the risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Patients using insulin pumps often report an increased sense of control over their diabetes. They can program the device to release a specific amount of insulin based on their carbohydrate intake and activity level. Such personalization enhances the efficacy of insulin therapy. The devices are compact and can be worn discreetly, which is another factor that many users appreciate.
Types of Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps can be classified primarily into two categories: traditional insulin pumps and closed loop insulin pumps. Each serves a distinct purpose and caters to differing user needs.
Traditional Insulin Pumps
Traditional insulin pumps continuously deliver a fixed rate of insulin, allowing users to bolus for meals or high blood sugar. The key characteristic of these pumps is their ability to provide customizable basal rates, which can be adjusted by the user according to their daily schedule.
Many choose traditional pumps for their reliability and simplicity. These pumps come with user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible for both new and experienced users. However, they require manual intervention to monitor glucose levels and adjust insulin delivery, which can be a limitation for some.
Some unique features of traditional pumps include:
- Adjustable insulin delivery rates based on personal needs.
- The option to program different basal rates for various times of the day.
- Compatibility with glucose monitors, although it may not be seamless.
Here are advantages and disadvantages of traditional insulin pumps:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- Flexible dosage adjustments.
- User-friendly.
- Requires manual monitoring of glucose levels.
- Possibility of insulin stacking, leading to hypoglycemia.
Closed Loop Insulin Pumps
Closed loop insulin pumps are often referred to as automated insulin delivery systems. They are designed to communicate with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems to automatically adjust insulin delivery according to real-time glucose levels. The primary feature of closed loop pumps is their ability to operate with minimal user input, significantly enhancing glycemic control.
Closed loop systems are a popular choice for many users who desire a hands-off approach to insulin management. These devices work collaboratively with CGM technology, enabling them to respond to fluctuating glucose levels automatically, reducing the chances of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.


Notable characteristics include:
- Automated insulin delivery based on CGM readings.
- Real-time adjustments, improving overall daily glucose control.
The advantages and disadvantages of closed loop systems are:
- Advantages:
- Disadvantages:
- Greater glycemic control.
- Less daily management required.
- Dependence on two devices (pump and CGM).
- Technical glitches can occur, requiring user vigilance.
Overall, understanding these insulin pump technologies is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. Each type offers unique benefits and poses specific challenges. Assessing these factors can lead to better management of diabetes, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Explained
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) plays a crucial role in diabetes management. It provides real-time data on blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their care. Users can react swiftly to rising or falling glucose levels, enhancing overall glycemic control. This section explores how CGM functions and the numerous benefits it offers to patients.
How CGM Works
Continuous glucose monitoring works through small sensors placed under the skin, usually on the abdomen or the arm. These sensors measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding cells. The sensors send data wirelessly to a receiving device, often a smartphone or a dedicated monitor.
Here’s a brief summary of how it operates:
- Sensor Insertion: A small device is inserted into the skin using a thin needle.
- Glucose Measurement: The sensor measures glucose levels at regular intervals, typically every few minutes.
- Data Transmission: Information is transmitted wirelessly to a receiver, alerting users to any concerning glucose trends.
- Alerts and Notifications: Users receive alerts for high or low glucose levels, allowing for timely intervention.
This process provides a more comprehensive view of glucose trends compared to traditional fingerstick testing, which captures only snapshots at specific times. CGM systems can significantly enhance patient autonomy and management capabilities.
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The benefits of continuous glucose monitoring are substantial and multifaceted. They include:
- Improved Glycemic Control: Real-time data helps users maintain their glucose levels within target ranges.
- Reduced Hypoglycemic Episodes: Immediate alerts for low sugar levels help prevent dangerous drops, fostering safety for individuals.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Users often report greater peace of mind knowing they have frequent updates on their glucose status.
- Better Decision-Making: With continuous data, individuals can make more informed dietary and activity choices, resulting in a healthier lifestyle.
- Empowerment: Access to detailed glucose trends empowers individuals to take charge of their diabetes management.
"CGM technology transforms the way individuals with diabetes manage their condition, shifting from reactive to proactive care."
Understanding CGM not only highlights its role within diabetes management systems but also emphasizes the need for continued education and adaptation among patients and healthcare professionals. As technology progresses, the integration of CGM with systems like closed-loop insulin pumps is likely to further enhance diabetes care.
Interconnection Between Closed Loop Pumps and CGM
The interplay between closed loop insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems represents a significant advancement in diabetes care. This integration is crucial for optimizing glycemic control and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By understanding how these systems work together, patients and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about diabetes management.
Defining Closed Loop Systems
Closed loop systems, often referred to as artificial pancreas systems, automate the delivery of insulin based on real-time glucose levels. These systems consist of three main components: an insulin pump, a continuous glucose monitor, and a control algorithm. The insulin pump delivers insulin subcutaneously while the CGM continuously tracks blood glucose levels. This feedback loop allows for dynamic adjustments in insulin delivery, responding to changes in glucose levels throughout the day.
The sophistication of these systems can vary. Some systems may only provide alerts when blood sugar levels are out of range, whereas others can automatically adjust insulin delivery without user intervention. The objective is to maintain blood glucose levels within a target range, minimizing the risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Interaction Between Insulin Pumps and CGM Devices
The interaction between insulin pumps and CGM devices is essential for effective diabetes management. When these technologies communicate, they create a synergistic effect that enhances patient outcomes. For example, when a CGM detects a drop in blood glucose levels, it can signal the insulin pump to reduce or halt insulin delivery, dramatically decreasing the likelihood of hypoglycemic episodes.
This synergy brings several benefits to users:
- Increased Convenience: Users experience less manual input, as the systems adjust automatically based on real-time data.
- Improved Accuracy: Continuous data allows for more precise insulin dosing, reducing the variability associated with traditional methods.
- Enhanced Safety: Real-time monitoring helps in potentially dangerous situations, alerting users to critical changes in glucose levels.
Despite these advantages, there are factors to consider. Technical difficulties, such as device malfunction or signal interference, can compromise performance. Moreover, effective use requires a certain level of health literacy, as users must understand how to interpret data from both devices.
"The integration of closed loop systems stands to redefine diabetes management, making control more accessible and less labor-intensive for patients."
By prioritizing user experience and maintaining open communication between devices, the interconnection between closed loop insulin pumps and CGM technologies can greatly enhance the management of diabetes while aiming for optimal health outcomes.
Dexcom Technology for Diabetes Management
In recent years, the role of continuous glucose monitoring has transformed diabetes management. Dexcom, as a leading provider, has revolutionized how patients interact with their glucose levels. The integration of Dexcom technology with closed loop insulin pumps represents a significant advancement in diabetes care, offering numerous benefits that enhance patient outcomes.
The current landscape of diabetes management continually evolves. Dexcom technology equips patients with real-time data regarding glucose levels, enabling better decision-making. This enhanced information flow allows users to respond proactively to fluctuations in blood sugar, a critical factor in managing diabetes effectively. The seamless integration of Dexcom devices with insulin pumps promotes a more automated approach, promoting optimal glycemic control and minimizing the risk of complications.
History and Development of Dexcom
Dexcom's journey in diabetes care began in the late 1990s, focusing on the continuous glucose monitoring landscape. The first Dexcom CGM device, Dexcom STS, was launched in 2006. This device marked a pivotal moment, as it allowed patients to gain insights into their glucose levels without the need for regular finger pricking.
Over the years, Dexcom has focused on refining the technology behind its monitors. In 2012, Dexcom G4 Platinum was introduced, featuring improved accuracy and reliability. This evolution continued with the launch of Dexcom G5 and G6, each iteration providing enhanced features such as smartphone compatibility and user-friendly interfaces.
Features of Dexcom Continuous Glucose Monitors


Dexcom's continuous glucose monitors come equipped with several notable features that address the needs of individuals managing diabetes:
- Real-time Glucose Monitoring: Patients receive updated glucose readings every five minutes, ensuring they are always aware of their current levels.
- Alerts and Notifications: The system can send alerts when glucose levels rise or fall beyond set thresholds. This functionality is crucial for preventing hypoglycemic events.
- Share Feature: Friends and family can view a user's glucose data in real-time, fostering a supportive environment for those with diabetes.
- Integration Capability: Dexcom devices can interface with various insulin pumps, including those with closed loop functionality, creating a more coordinated approach to management.
- User-friendly App: The Dexcom app is designed to provide accessible data interpretation, allowing users to understand trends in their glucose levels easily.
"Continuous glucose monitoring changes the game in diabetes management, providing data that empowers patients to make informed decisions." – Medical Expert
Advantages of Using Closed Loop Systems
The integration of closed loop insulin pump systems with continuous glucose monitoring technologies has marked a significant advancement in diabetes management. These systems offer numerous advantages for individuals struggling to maintain their blood sugar levels within target ranges. This section will detail the critical benefits associated with using closed loop systems, focusing specifically on enhanced glycemic control and the reduction in hypoglycemic events. Understanding these advantages can provide valuable insights for patients, healthcare providers, and researchers in the field of diabetes care.
Enhanced Glycemic Control
One of the primary benefits of closed loop systems is their ability to enhance glycemic control. These systems continuously monitor glucose levels and adjust insulin delivery based on real-time data. This automatic adjustment helps maintain blood glucose levels within a narrow range.
Research indicates that individuals using closed loop insulin pumps often experience lower HbA1c levels compared to those relying on manual insulin administration. Lower HbA1c is associated with a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy and retinopathy.
Key Factors of Enhanced Control:
- Real-Time Data: Closed loop systems provide continuous feedback, allowing for timely insulin administration.
- Algorithm-Driven Adjustments: Advanced algorithms calculate the appropriate insulin dosage based on individual needs.
- Reduced Variability: These systems contribute to less fluctuation in glucose levels, leading to more stable day-to-day management.
The ability to achieve enhanced glycemic control through closed loop systems can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
Reduction in Hypoglycemic Events
Another noteworthy advantage of closed loop systems is the significant reduction in hypoglycemic events. Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can be dangerous and lead to serious health complications if not managed promptly. With the automatic nature of closed loop systems, the risk of hypoglycemia can be minimized.
These systems monitor glucose levels continuously, allowing for adjustments in insulin delivery before blood sugar levels drop too low. This proactive approach not only prevents acute episodes of hypoglycemia but also alleviates the anxiety often associated with managing diabetes.
Insights on Hypoglycemic Reduction:
- Predictive Alerts: Many closed loop systems provide alerts and warnings, indicating a potential hypoglycemic event before it occurs.
- Consistent Monitoring: Continuous glucose monitoring allows for more accurate detection of trends that may lead to hypoglycemia.
- Personalized Insulin Dosing: The systems can be configured to handle individual responses to insulin, further reducing the risk of lows.
In summary, closed loop systems play an essential role in managing diabetes, particularly in enhancing glycemic control and reducing the occurrence of hypoglycemic events. These advantages are critical for patients seeking both improved health outcomes and an enhanced quality of life.
The implementation of closed loop insulin pumps is paving the way for smarter and safer diabetes management, revolutionizing how individuals manage their condition.
Understanding these advantages can be a powerful tool for patients and healthcare providers in optimizing diabetes management strategies.
Challenges in Closed Loop Diabetes Management
Closed loop systems in diabetes management are not without their obstacles. Understanding the challenges is crucial for evaluating their effectiveness and potential before diving deeper into the integration of technology in insulin delivery. While the benefits are numerous, it is essential to recognize that these systems require significant consideration regarding technical difficulties and user engagement.
Technical Difficulties
One of the foremost challenges faced in closed loop systems is the technical complexities involved in their design and operation. These systems rely heavily on accurate data exchange between the insulin pump and continuous glucose monitoring devices. Any disruption in communication can lead to inaccurate insulin delivery, potentially resulting in hypo or hyperglycemic episodes.
Moreover, hardware malfunctions are a concern. Components such as sensors and pumps must be reliable and well-calibrated. Issues such as battery life and software compatibility can create barriers to smooth functionality. For example, if a sensor fails to provide accurate glucose readings, the insulin pump cannot deliver the appropriate dose. These technical difficulties necessitate regular maintenance, updates, and sometimes replacement of devices, which can be a burden for users.
"The reliability of technology is paramount in closed loop systems. Users need assurance that their devices will function correctly to manage their diabetes effectively."
The need for user education on troubleshooting can also arise. Users might find themselves in situations where they need to intervene manually if the system fails or produces erratic results. Technical troubleshooting skills become vital, emphasizing the need for comprehensive training during initial device setup.
User Compliance and Education
Equally important in closed loop diabetes management is user compliance and education. The sophistication of these systems requires users not only to understand how the devices work but also to commit to regular usage and monitoring. Many patients new to closed loop technology may find it overwhelming. A lack of confidence can lead to non-compliance with therapy, reducing the system's overall effectiveness.
Education plays a pivotal role. Healthcare providers must ensure patients are well-informed about the functionality of their devices as well as the potential risks and benefits. Comprehensive training should address not only the basic operation but also lifestyle adjustments that users may need to embrace. Charts detailing blood glucose trends, dosage adjustments based on activity level, and dietary considerations can support this education.
Furthermore, the support extended by healthcare providers is critical. Regular check-ins can help address any concerns and reinforce best practices. Patients feeling engaged and supported are more likely to adhere to treatment regimens effectively.
By addressing these challenges, both technical and educational, the use of closed loop systems can be optimized, ultimately enhancing diabetic care and user satisfaction.
Future of Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring
The future of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring is a critical area to explore in diabetes management. As technology evolves, it brings with it a transformation in how individuals manage their condition. Closed loop systems, integrated with continuous glucose monitors, are at the forefront of this development. These technologies promise to change the landscape of diabetes care significantly, allowing for more precise insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings.
In this article, we will discuss emerging innovations and their potential impact on patient outcomes. A better understanding of these advancements can illuminate the direction in which diabetes management is heading.
Innovations on the Horizon
Recent advancements in insulin delivery systems and glucose monitoring hold promise for improving treatment standards. For instance, smart insulin pens are gaining popularity. They utilize Bluetooth technology to connect with smartphones, allowing for real-time data tracking. Additionally, new wearable devices are being developed, which can provide insights into meal impacts on blood sugar levels.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI capabilities are being integrated into closed loop systems. These systems analyze data patterns and provide personalized insulin dosing recommendations.
- Biopatches: Research into biocompatible patches for insulin delivery is ongoing. These patches could deliver insulin through the skin with minimal invasiveness, providing a painless alternative to traditional injections.
- Automated Insulin Delivery: Systems that automatically adjust insulin based on continuous glucose data are rapidly advancing. This reduces the need for manual adjustments by the user, improving convenience and consistency.
These innovations reflect a trend towards making diabetes management more user-friendly and efficient.


Potential Impact on Patient Outcomes
The integration of advanced insulin delivery and glucose monitoring technologies can significantly alter patient outcomes. Improved glycemic control may reduce the risks associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular diseases and neuropathy.
- Increased Time in Range: With real-time monitoring and automated adjustments, patients may experience fewer fluctuations in glucose levels. Studies suggest that achieving more stable glucose levels can lead to a reduction in long-term complications.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: As these technologies minimize the burden of constant monitoring and management, users often report a better quality of life. The freedom from frequent finger pricks and daily calculations can lead to less anxiety and stress.
- Patient Empowerment: With better tools comes better education and understanding of one’s condition. Patients empowered with knowledge and technology are more likely to adhere to treatment regimens and make informed lifestyle choices.
The integration of technology in diabetes management provides a multi-faceted approach to care, potentially leading to improved health outcomes and overall patient satisfaction.
In summary, the innovations in insulin delivery and glucose monitoring represent a significant step towards comprehensive diabetes management. The focus continues to be on refining these technologies for better outcomes.
For more information on diabetes management advancements, visit Wikipedia or Britannica.
Patient Perspectives on Closed Loop Systems
Understanding the views and experiences of users is a crucial aspect when discussing closed loop insulin pump systems. Patients' perspectives provide insight that goes beyond the technical specifications and functionalities of these devices. The lived experiences shape how these technologies are adopted and how effective they are perceived to be in daily life management. A focus on patient feedback reveals key benefits, challenges, and areas for improvement in closed loop systems.
User Experiences and Feedback
Patients utilizing closed loop systems often report a significant impact on their glycemic control. Many users note improvements in their overall management of diabetes, citing a reduction in fluctuations in their blood sugar levels. This stability leads to fewer episodes of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, providing users with greater peace of mind.
Some specific experiences shared by users include:
- Increased Confidence: Users feel more secure managing their diabetes and are less anxious about their blood glucose levels.
- Convenience: The automation of insulin delivery reduces the burden of constant monitoring. Users can engage more freely in daily activities without interruption.
- Quality of Life: Many report a noticeable enhancement in their daily lifestyle, allowing them to focus on other personal and professional pursuits.
However, not all feedback is positive. Some patients experience technical issues or a learning curve when integrating closed loop systems into their routines. Initial setup can be complex, and not all users feel adequately supported through their transition. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that patients receive comprehensive training to alleviate these challenges.
"Closed loop technology has changed my routine for the better, but I needed time and guidance to really understand how to use it effectively." - Anonymous User
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Methods
When comparing closed loop systems to traditional methods of diabetes management, several distinct advantages and disadvantages become apparent. Traditional methods often involve manual insulin administration and rudimentary blood sugar checks, leading to less efficient regulation of glycemic levels. Here are some key differences:
- Automation: Closed loop systems automate the insulin delivery process based on real-time glucose readings, unlike traditional methods that require constant manual inputs.
- User Error: The potential for human error with traditional monitoring—such as miscalculating doses—reduces substantially with closed loop systems. This shift can greatly enhance accuracy in glucose management.
- Data Integration: Closed loop systems often have integrated monitoring and control, which provides comprehensive data analysis for better personalized management.
Despite these advantages, traditional methods still hold value for certain patient populations. Some individuals may prefer a hands-on approach and appreciate the direct control over their insulin management. It is essential to recognize that each method has its unique benefits and potential drawbacks, making it important for healthcare providers to offer tailored solutions based on individual patient needs.
Ultimately, the transition to closed loop technology is not merely a technical adjustment but a significant lifestyle change for users. Understanding patient perspectives is fundamental to enhancing these systems and ensuring better outcomes in diabetes management.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in the effective implementation and management of closed loop insulin pump systems and Dexcom technology. Their involvement significantly influences patient outcomes and the overall success of diabetes management plans. Providers serve as the primary source of knowledge, support, and ongoing care, ensuring patients understand the functionalities and advantages of these devices. This section examines how healthcare practitioners can facilitate the integration of these advanced technologies into patient care, as well as the responsibilities and benefits associated with this collaboration.
Training and Support for Patients
Training patients on how to use closed loop insulin pumps and Dexcom continuous glucose monitors is vital. This training should not only cover the operational aspects but also the significance of proper usage in achieving better glycemic control. Proper training often includes the following elements:
- Instruction on device functionality and setup.
- Understanding of glucose monitoring data and insulin delivery.
- Strategies for troubleshooting common issues.
- Guidance on lifestyle modifications that can enhance device efficacy.
Providers should offer adjustable training sessions that align with the individual learning pace of each patient. Continuous support through follow-up appointments or online platforms can help address concerns and reinforce skills. This ongoing support is particularly beneficial, as many patients may find it challenging to adapt to new technologies initially.
Monitoring and Adjustment Protocols
Monitoring and adjustment protocols are essential components in the management of diabetes with advanced devices. Healthcare providers must establish comprehensive monitoring systems to oversee patients' glucose levels, insulin delivery, and overall performance of the closed loop system. These protocols should encompass the following aspects:
- Regular reviews of glucose data generated by Dexcom monitors.
- Assessment of insulin pump performance and adjustments based on feedback from patients.
- Modification of treatment plans in response to changes in lifestyle, diet, or health status.
Effective monitoring allows for timely interventions and can reduce the risk of complications. Providers need to create a feedback loop with patients, encouraging them to report any anomalies or concerns they experience with their devices.
"Proper monitoring and engagement significantly elevate patient confidence in managing their diabetes with technology."
By prioritizing patient education and establishing effective monitoring protocols, healthcare providers can optimize the use of closed loop insulin pumps and Dexcom technology, enhancing the quality of care and improving patient outcomes.
Regular communication and trust between healthcare providers and patients also play an integral role. A well-informed patient is generally more engaged and proactive, leading to better management of their condition.
End
In this article, we have explored the dynamic relationship between closed loop insulin pumps and Dexcom technology. The importance of this topic cannot be overstated, as the integration of these systems represents a significant advancement in diabetes management. Through various discussions, we examined how closed loop systems utilize continuous glucose monitoring to adjust insulin delivery automatically and effectively. This coordination enhances glycemic control, decreases the risks of serious complications, and ultimately improves the quality of life for diabetes patient.
Summary of Key Findings
Key findings of this article include:
- Integration Benefits: Closed loop insulin pumps significantly improve glycemic control by reacting to real-time glucose data from Dexcom devices. This automated adjustment minimizes the need for constant manual input.
- User Experience: Many users report higher satisfaction and confidence in managing their diabetes with these technologies. Their ability to provide insights leads to better decision-making for daily insulin management.
- Challenges: Despite the advantages, users and clinicians face issues such as technical difficulties and the need for ongoing education to maximize the benefits of these systems.
These findings reveal the potential of combining these technologies to create a more effective diabetes management ecosystem.
Call to Action for Further Research
Further research into closed loop insulin pumps and Dexcom technology is essential for a deeper understanding of their long-term effects and potential enhancements. Key areas for exploration include:
- User Compliance: Investigating factors that affect user adherence to therapy can provide insights on how to enhance engagement with these systems.
- Technological Innovations: Researching advancements in sensor accuracy and pump algorithms could lead to smarter systems that better meet patient needs.
- Patient-Centric Studies: Engaging patients in studies to gather their experiences and feedback will shed light on real-world challenges and promote strategies for improvement.
The future of diabetes management hinges on robust research, innovation, and collaboration among patients, healthcare providers, and technology developers. Enhancing these systems can lead to significantly improved healthcare outcomes.



