Understanding the Achilles Cushion: A Comprehensive Analysis

Intro
The Achilles cushion has gained attention in recent years for its pivotal role in human biomechanics. Understanding this structure is essential for comprehending how we navigate various physical activities. This cushion acts as a shock absorber, reducing the impact on the heel during high-impact activities like running and jumping. Furthermore, the Achilles cushion is also vital in preventing injuries and facilitating effective rehabilitation processes.
In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the intricate details of the Achilles cushion, examining its anatomy, function, and clinical significance. We will explore the disorders that may affect its performance and discuss various treatment and rehabilitation strategies. Research advancements provide us with new insights, which will also be covered.
This narrative aims to enrich the knowledge base for students, researchers, educators, and professionals interested in musculoskeletal health and the mechanics of movement. With this focus, we will highlight key findings regarding the Achilles cushion, elucidate various methodologies employed in research, and synthesize the information presented throughout the article.
Research Highlights
Key Findings
- The Achilles cushion plays a significant role in reducing forces experienced by the heel during ambulation.
- Various studies indicate that effective cushioning can reduce the incidence of common injuries such as Achilles tendinopathy and plantar fasciitis.
- The interplay between tissue composition and biomechanical performance is critical for maintaining overall foot health.
Implications and Applications
The findings underscore the importance of the Achilles cushion not just in athletics, but in everyday activities as well.
- Injury prevention: Understanding the mechanics can lead to better preventative measures in both recreational and professional athletes.
- Rehabilitation strategies: Tailoring specific exercises helps enhance recovery and restores normal function in affected individuals.
"Research into the Achilles cushion is informing new rehabilitation approaches that can significantly enhance recovery times for athletes and active individuals."
Methodology Overview
Research Design
Research typically employs both qualitative and quantitative approaches to fully understand the Achilles cushion. Experimental designs focus on anatomical studies, biomechanical analyses, and clinical trials. This allows researchers to gather a thorough understanding of tissue function and performance.
Experimental Procedures
Common practices include:
- Imaging Techniques: MRI and ultrasound imaging provides insight into the structure and condition of the Achilles cushion.
- Biomechanical Assessment: Force plates measure impact forces during activities, helping to analyze the cushion's performance.
- Clinical Trials: These trials assess the effectiveness of various treatment strategies in addressing disorders related to the Achilles cushion.
This layered approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the cushion's significance in human biomechanics and health.
Prelims to the Achilles Cushion
The Achilles cushion serves as a vital component within the musculoskeletal system, primarily influencing movement and mobility in humans. Understanding this tissue's multifaceted role is essential for those studying biomechanics, rehabilitation, and athletic training. The significance of the Achilles cushion cannot be overstated, as it helps absorb impact during activities, reducing stress on connected structures like tendons and ligaments.
Definition and Overview
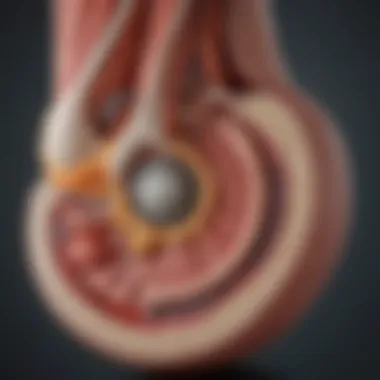
The Achilles cushion is a fibroelastic structure located in the posterior aspect of the ankle. Formed largely by the Achilles tendon and surrounding tissues, it functions as a shock absorber during high-impact activities. Comprising specialized cells and an extracellular matrix, the cushion plays a critical role in cushioning the forces exerted on the foot and ankle. By redistributing impact forces, it helps prevent injuries and enhance performance.
The concept of the Achilles cushion is not just about its structural attributes but also its implications for overall mobility and functionality. Understanding how the Achilles cushion operates allows for better-informed choices regarding footwear, training regimens, and injury prevention strategies. Ultimately, a deep comprehension of this cushion can lead to improved rehabilitation approaches, promoting optimal recovery and enhanced athletic performance.
Historical Context
Historically, the study of the Achilles cushion can be traced back to early anatomical explorations of the foot and ankle. Most traditional texts focused primarily on the anatomical elements, often neglecting their functional significance. Over the years, research expanded, looking beyond mere structure to focus on biomechanics.
In the latter half of the 20th century, investigations into tendinopathy and related injuries brought renewed attention to the Achilles region. Researchers began to explore the relationship between anatomy, function, and the development of disorders affecting the Achilles cushion. Such research insights have led to advancements in understanding how to conserve and rehabilitate this important area of the human body.
Over time, a more profound respect for the role of this anatomical structure has emerged within the sports medicine field. Understanding the historical limitations in the study of the Achilles cushion has helped fuel modern investigations, now focusing on biopsychosocial aspects surrounding injury prevention and management strategies.
Anatomy of the Achilles Cushion
The anatomy of the Achilles cushion is fundamental to understanding its role in human biomechanics. This section explores how the structure contributes to its function, emphasizing aspects such as the interplay between different components and their significance in maintaining mobility and preventing injuries. Understanding the anatomy allows insight into common ailments and guides effective treatment strategies.
Structural Composition
Cellular Components
Cellular components are the basic building blocks of the Achilles cushion. This structure includes various cell types, such as fibroblasts and tenocytes, which are crucial for tissue maintenance and repair. Fibroblasts play a key role in producing collagen, while tenocytes are essential for the health of tendons.
A significant characteristic of these cells is their responsiveness to mechanical stress. This responsiveness is beneficial because it allows the Achilles cushion to adapt to varying physical demands. However, when subjected to excessive stress, these cells can become damaged, leading to potential disorders.
The unique feature of cellular components in the Achilles cushion lies in their ability to regenerate. This regenerative capacity is advantageous as it supports recovery after injuries. However, it can also pose a downside; if stress continues without appropriate interventions, the potential for chronic conditions increases.
Extracellular Matrix
The extracellular matrix provides structural and biochemical support to the Achilles cushion. Composed of proteins and polysaccharides, it serves as a scaffold for cells, facilitating their functions. A key characteristic of the extracellular matrix is its elasticity, which allows the tissue to withstand compression and tensile forces.

This property makes the extracellular matrix a crucial element for shock absorption, which is vital for activities involving repeated impacts. The matrix's unique feature of containing glycosaminoglycans contributes to hydration and lubrication, ensuring smooth movement within the joint structure. This offers advantages, such as enhanced mobility, though its composition can be affected by both age and injury, impacting its effectiveness in cushioning.
Location and Connectivity
The Achilles cushion is situated at the posterior aspect of the heel, connecting the heel bone to the calf muscles. Its strategic location is significant because it directly influences how forces are transmitted during activities like walking and running. The cushion serves as a protective barrier, absorbing shocks and reducing strain along the Achilles tendon.
Moreover, the connectivity of the Achilles cushion with surrounding tissues, including muscles and tendons, is essential for functional integration. Disruptions in this connectivity can lead to discomfort and disorders, highlighting the importance of maintaining its integrity in athletic contexts and daily activities. Understanding these anatomical relationships is crucial for developing effective prevention and rehabilitation strategies.
Functional Role of the Achilles Cushion
The Achilles cushion is integral to understanding human movement and overall biomechanics. Its roles are multifaceted, encompassing the mechanics of movement, shock absorption, and the facilitation of mobility. By exploring these aspects, one can appreciate the cushion's significance not only in daily activities but also in athletic performance and injury prevention. The unique attributes of the Achilles cushion contribute to its primary functions, enabling it to support the human body's dynamic requirements.
Biomechanics of Movement
The biomechanics of movement is fundamentally linked with the operation of the Achilles cushion. This anatomical feature aids in the execution of varying physical activities that demand precise motility and strength. The cushion provides a critical point for the interaction between tendons and bones, effectively managing the forces generated during movement. During walking, running, or jumping, it absorbs pressure that otherwise would impact the heel and subsequently the rest of the body.
The design of the Achilles cushion permits a degree of elasticity, allowing it to deform under load while maintaining its structure. This ability is essential for the transfer of forces throughout the kinetic chain, ensuring that motions remain efficient. By optimizing the energy storage during the push-off phase in a gait cycle, the Achilles cushion enhances performance significantly.
Shock Absorption
Shock absorption is one of the primary functions of the Achilles cushion. The human body encounters various forms of shock through activities like running or jumping. Without effective shock absorption, these impacts can lead to debilitating injuries, affecting mobility and overall quality of life. The Achilles cushion plays a crucial role here, mitigating the stress transmitted to adjacent structures such as the heel bone and lower leg.
Research indicates that the material properties of the Achilles cushion, including its cellular makeup, are designed to dissipate forces effectively. This anatomical structure accommodates both vertical and horizontal forces, redistributing impact stress. Such capabilities are vital in preventing microtrauma over time, which can lead to conditions like tendinopathy or bursitis.
"The ability of the Achilles cushion to absorb and manage shock is crucial for sustaining mobility and preventing injury."
Facilitating Mobility
Facilitating mobility is another significant role of the Achilles cushion. Its structural and functional characteristics allow for a smoother range of motion, making it a key player in ambulation. When the Achilles cushion operates effectively, it provides stability and support for the heel's movements, which is particularly important in activities requiring swift direction changes, like sports.
The cushion not only aids in supporting the foot but also enhances proprioceptive feedback, which is essential for balance and coordination. This sensory feedback is integral in tasks that require precise movements. Therefore, impairments related to the Achilles cushion can result in decreased mobility and an increased risk of falls or injury.
In summary, the functional role of the Achilles cushion is critical to biomechanical efficiency, injury prevention, and overall mobility. This structure not only withstands and absorbs shocks but also facilitates reliable movement patterns that are necessary for a healthy, active lifestyle.
Common Disorders Associated with the Achilles Cushion
Understanding common disorders that affect the Achilles cushion is crucial in recognizing the implications these conditions can have on overall mobility and health. The Achilles cushion, being integral to movement, can be impacted by various disorders that lead to pain, inflammation, or structural damage. Awareness of these conditions helps in early diagnosis and effective treatment, which is essential for recovery and maintaining functionality. The subsequent subsections will detail three prominent ailments: tendinopathy, bursitis, and tear and rupture. Each has unique characteristics, yet all share a connection to the Achilles cushion. Identifying these issues is the first step toward enhancing musculoskeletal health in individuals, especially active populations.
Tendinopathy
Tendinopathy is a condition characterized by the degeneration of the Achilles tendon, often resulting from overuse. This disorder is prominent among athletes and individuals engaging in repetitive activities, such as running or jumping. The pain associated with tendinopathy can be debilitating and may lead to decreased mobility.
Symptoms of tendinopathy typically include:
- Pain during activity that gradually worsens
- Swelling around the tendon
- Stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity
- Tenderness when touching the tendon
The underlying mechanism involves a combination of micro-tears in the tendon, leading to inflammation and disruption of collagen fibers. In many cases, overtraining or improper footwear contributes to the development of this disorder. Thus, appropriate training regimens and orthotic support are vital. Treating tendinopathy often includes:
- Physical therapy focused on strengthening and stretching
- Rest to allow healing
- Pain management strategies, including ice application
Bursitis
Bursitis of the Achilles region occurs when the bursa, a small sac filled with fluid, becomes inflamed. This condition can be particularly bothersome and is often mistaken for tendinopathy due to similar symptoms.
Common signs of bursitis include:
- Localized swelling
- Tenderness near the heel
- Pain during movement or pressure on the area
Bursitis can result from repetitive strain, excessive pressure during activities, or even certain footwear styles. Changes in training intensity and using proper footwear can aid in prevention. Treatment typically involves:
- Resting the affected area
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation
- In some severe cases, aspiration of the bursa may be necessary
Tear and Rupture
Tears and ruptures of the Achilles tendon are critical conditions that demand immediate attention. A complete rupture can occur suddenly, often during high-impact activities. Individuals may hear a distinct popping sound when the rupture happens, followed by intense pain.
Signs of a tear or rupture may include:
- Severe pain in the back of the leg
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg
- Swelling and bruising around the tendon
These injuries typically occur without prior symptoms, making them particularly alarming. Mechanically, they arise from forces that exceed the tensile strength of the tendon material, often exacerbated by pre-existing conditions like tendinopathy. Treatment options can range from:
- Surgical intervention in complete ruptures
- Conservative management, involving immobilization and rehabilitation for partial tears


Early recognition and treatment of these Achilles cushion disorders are critical in preventing long-term complications and improving quality of life.
Risk Factors for Achilles Cushion Disorders
Understanding the risk factors associated with disorders of the Achilles cushion is crucial for both prevention and early detection. The Achilles cushion, primarily composed of dense connective tissue, provides vital support during movement and absorbs forces. When we explore the factors affecting the Achilles cushion, we can discern how them might lead to specific injuries. This understanding is not just academic but serves practical purposes for athletes, healthcare professionals, and individuals engaged in regular physical activity.
Biomechanical Factors
Biomechanical factors significantly contribute to the health of the Achilles cushion. These factors include improper foot mechanics, alignment issues, and gait abnormalities. An individual with overpronation, for instance, places excess stress on the Achilles tendon and the associated cushion. This abnormal load distribution can compromise the durability of tissues, leading to injuries like tendinopathy. Moreover, structural deformities such as flat feet or high arches can further exacerbate the risk of cushion-related disorders.
The assessment of these biomechanical characteristics is essential. Through methods like gait analysis and pressure mapping, practitioners can identify abnormal patterns. Subsequently, corrective measures, such as orthotic devices, can be implemented to relieve undue strain.
Training and Activity Level
The relationship between training intensity, frequency, and the condition of the Achilles cushion cannot be overlooked. Individuals engaging in high-impact sports, such as sprinting or basketball, face greater risks. Rapid increases in workload or inappropriate training regimens can overwhelm the Achilles cushion. Those who fail to adequately warm up or do not incorporate sufficient rest periods may find themselves at a higher risk of injury.
For athletes and active individuals, balancing intensity with recovery is vital. A well-structured training program that includes gradual progressions can significantly mitigate risks. Education on proper techniques and cross-training may also contribute to a more resilient Achilles region.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender are additional determinants of the likelihood of developing disorders affecting the Achilles cushion. As people age, the elasticity of the connective tissues tends to diminish. This reduces the cushioning effect and, as a result, increases vulnerability to injuries. Older adults often experience conditions such as tendinopathy simply due to age-related changes in collagen structure and function.
Gender considerations are also pertinent; research indicates that women may be more susceptible to certain Achilles-related conditions. Hormonal differences may influence connective tissue characteristics, subsequently impacting the cushion's integrity.
Static awareness of these factors enables effective prevention strategies tailored to age and gender demographics.
Understanding and addressing these risk factors is paramount to maintaining the integrity of the Achilles cushion and preventing related disorders.
By recognizing and mitigating the risks associated with biomechanical issues, training regimens, and demographic influences, individuals can enhance not only the health of their Achilles cushion but also their overall mobility and athletic performance.
Diagnostics of Achilles Cushion Disorders
Understanding the diagnostic processes for disorders related to the Achilles cushion is fundamental for effective treatment and management. Proper diagnosis informs healthcare providers about the nature and extent of the injury, guiding appropriate interventions. This section explores various diagnostic techniques that are used to assess injuries at the Achilles cushion.
Clinical Evaluation Techniques
Clinical evaluation is often the first step in diagnosing Achilles cushion disorders. A thorough medical history and physical examination are vital in identifying symptoms experienced by the patient. Healthcare providers typically assess the range of motion, tenderness, and swelling in the Achilles area.
A comprehensive clinical evaluation may involve:
- Patient History: Discussing previous injuries, training regimens, and pain onset.
- Physical Assessment: Checking for any abnormalities in gait, as well as observing ankle and calf strength.
- Palpation: Gently feeling the Achilles tendon and surrounding areas for signs of inflammation or abnormalities.
These methods help provide initial insights into the condition, allowing practitioners to decide on further imaging tests or specialized assessments.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging techniques are essential tools in the diagnostic process. They provide detailed visual information about the structure and function of the Achilles cushion and surrounding tissues. Two common imaging modalities used are ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging is valuable in assessing soft tissue structures, making it an effective option for examining the Achilles cushion.
- Key Characteristic: Its real-time imaging capability allows clinicians to observe dynamic movement, which aids in understanding the extent of any injury.
- Benefits: Ultrasound is non-invasive, requires no radiation, and is relatively accessible compared to other imaging methods. It is particularly beneficial for guiding injections or monitoring conditions over time.
- Unique Feature: The ability to visualize fluid collections or tears in real-time enhances diagnostic accuracy.
- Advantages/Disadvantages: While ultrasound is advantageous due to its immediacy and non-invasive nature, its effectiveness can be limited by the operator's skill and patient factors such as body habitus.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is another essential diagnostic tool. It provides high-resolution images of the soft tissue structures in the foot and ankle, including the Achilles tendon and cushion.
- Key Characteristic: MRI offers detailed images, critical for identifying subtle injuries or chronic changes that may not be visible on ultrasound.
- Benefits: It is particularly useful for evaluating complex or longstanding cases where other imaging modalities may not provide sufficient information.
- Unique Feature: MRI can differentiate between various types of soft tissue injuries, assisting in accurate diagnosis.
- Advantages/Disadvantages: However, MRI is more time-consuming, typically more expensive, and involves patient exposure to a magnetic field, which may limit its use in certain populations.
The choice of imaging modality often depends on the specific clinical scenario, the patient's history, and the initial clinical evaluation findings.
Treatment and Rehabilitation Strategies
Effective treatment and rehabilitation strategies are crucial in addressing disorders related to the Achilles cushion. These approaches aim to alleviate pain, restore function, and improve quality of life for individuals affected by issues such as tendinopathy, bursitis, or more severe injuries such as tears and ruptures. Both conservative and surgical options offer distinct benefits and are chosen based on the severity of the condition, patient’s overall health, and personal preferences.
Conservative Management Approaches
Conservative management strategies often serve as the first line of treatment for Achilles cushion disorders. They focus on non-invasive methods to relieve symptoms and promote healing.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in rehabilitation. It helps individuals regain strength and flexibility around the Achilles cushion. One key characteristic of physical therapy is its tailored exercise programs that address specific muscular imbalances. This makes it a popular choice for many recovering from Achilles-related injuries.


A unique feature of physical therapy is the hands-on techniques used by professionals to manipulate the tissue. These techniques can enhance blood flow and promote healing. The advantages include reduced recovery time and improved mobility. However, it requires active participation and commitment from the patient.
Orthotic Devices
Orthotic devices can significantly assist in treatment by providing necessary support and cushioning. These devices help redistribute pressure away from the Achilles cushion, which can reduce pain and prevent further injury. Their key characteristic is their ability to customize fit according to the user's specific needs.
The unique feature of orthotic devices is their versatility. They can be used in various types of footwear, ensuring comfort across different activities. The advantages of using orthotic devices are increased support and improved biomechanics during movement. However, they may require adjustments and can sometimes feel bulky.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical interventions may be necessary. These procedures aim to repair damaged tissue, relieve pain, and restore function. Surgical options can include debridement, Achilles tendon repair, or resection of painful bursa. Surgery often yields quicker results when performed appropriately but usually involves longer recovery time. Decisions regarding surgery should always be discussed thoroughly with healthcare professionals.
"Timely intervention and appropriate treatment strategies are essential for maintaining the health of the Achilles cushion. They not only enhance recovery but can prevent long-term complications."
Recent Advances in Research
Research related to the Achilles cushion has undergone significant transformation in recent years. These advances are critical, as they not only improve our understanding of the tissue's role in human biomechanics, but also influence how we approach treatment for associated disorders. Increased understanding leads to better preventive and rehabilitative strategies, which is vital for athletes and individuals engaged in physical activities.
Innovative Treatment Modalities
In the realm of innovative treatment modalities, recent studies have focused on non-invasive approaches that leverage technology to enhance recovery processes. Treatments such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy have gained attention. PRP therapy uses components of the patient's own blood to promote healing and reduce inflammation in the Achilles area. This approach minimizes the risk of complications compared to more invasive surgical options.
Another modality is the use of shockwave therapy, which utilizes acoustic waves to stimulate healing in damaged tissues, including the Achilles cushion. This technique helps reduce pain and improves mobility, making it a promising option for those suffering from chronic discomfort or injuries.
Additionally, regenerative medicine techniques, such as stem cell injections, are being explored. These strategies aim to harness the body’s innate healing capabilities, potentially leading to enhanced recovery times and improved functional outcomes. Treatment based on biomechanical assessments, including customized orthotics and footwear adjustments, is also vital. This allows for a tailored approach that addresses the specific needs of the individual, further supporting therapeutic efficacy.
Longitudinal Studies and Insights
Longitudinal studies have provided critical insights into the long-term implications of Achilles cushion health. Such studies track individuals over extended periods, examining how changes in loading patterns, activity levels, and age affect the Achilles cushion. Findings from these investigations are essential. They reveal risk factors for degeneration and injury, while also highlighting the importance of proactive interventions.
For example, a longitudinal study may reveal that individuals who regularly engage in high-impact sports have a higher incidence of tendinopathy. By identifying these patterns, healthcare professionals can develop targeted preventive measures. These could include educational programs focusing on proper technique and biomechanics in physical activities.
In addition, longitudinal research aids in understanding recovery trajectories. It helps professionals predict how quickly individuals might return to their sport or activities after injury. Such information is invaluable when setting rehabilitation goals and establishing realistic timelines for patients.
Preventive Strategies for Achilles Cushion Health
Preventive strategies for maintaining the health of the Achilles cushion are critical for individuals engaged in physical activity. Recognizing the significance of these strategies can greatly influence mobility and overall well-being, particularly for athletes and active individuals. In this section, we will discuss tailored exercise regimens and footwear considerations as effective measures to safeguard against potential injuries and disorders associated with the Achilles area.
Tailored Exercise Regimens
Developing specific exercise regimens can enhance the strength and flexibility of structures surrounding the Achilles cushion. These regimens should be individualized based on personal fitness levels and injury history. A proper routine may include:
- Calf Raises: Strengthening the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles assists in providing better support to the Achilles tendon.
- Eccentric Exercises: These exercises focus on lengthening the muscle under load, aiding in recovery and reducing the risk for tendinopathy.
- Stretching: Regular stretching of the calf muscles can improve range of motion and help prevent stiffness.
Incorporating these elements into a regular workout plan allows for progressive overload, which is crucial for adaptation and strengthening the region, thus reducing injury risks. It is also important to emphasize warm-up and recovery periods, ensuring that muscles are properly prepared for physical activity.
Footwear and Equipment Considerations
Choosing the right footwear plays a vital role in preventing injuries related to the Achilles cushion. Optimal shoes should provide adequate support and cushioning while accommodating the arch and foot structure. Important factors to consider include:
- Cushioning: Shoes that offer sufficient cushioning help absorb impact forces, reducing stress on the Achilles structure.
- Stability: Proper arch support is critical. Footwear must stabilize the foot without compromising mobility.
- Fit: A well-fitted shoe can prevent excessive movement of the foot within the shoe, minimizing the risk of friction or tears to the Achilles region.
In addition, considering the use of specialized equipment, such as orthotic inserts, can address biomechanical deficiencies. These devices provide customized support, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions affecting their gait.
"Preventive strategies are not just about avoiding injury; they are also about enhancing performance and longevity of the soft tissues involved."
To summarize, prioritizing tailored exercise regimens and appropriate footwear can profoundly contribute to the maintenance of Achilles cushion health. Educating individuals on these preventive measures empowers them to take charge of their physical well-being.
The End and Future Directions
The exploration of the Achilles cushion is essential due to its significant role in human biomechanics, especially in activities characterized by repetitive impact such as running and jumping. Understanding the multifaceted functions of the Achilles cushion aids in the prevention and management of various disorders that can arise from its dysfunction. In this section, we examine the primary takeaways from our analysis and discuss future areas for research and application in clinical practice.
Summary of Key Takeaways
The Achilles cushion is not merely a passive structure; it is an active component in both mobility and injury prevention. Key points from our analysis include:
- Anatomical Significance: The Achilles cushion is integral to the tendons and muscles that facilitate movement, providing necessary support and cushioning during physical activities.
- Common Disorders: Understanding conditions such as tendinopathy and bursitis is crucial for timely intervention and rehabilitation.
- Risk Factors: Biomechanical factors, training regimens, and demographic elements like age and gender significantly influence the likelihood of developing disorders related to the Achilles cushion.
- Treatment Modalities: A variety of conservative management approaches, including physical therapy and orthotic support, alongside surgical options, underscore the importance of personalized treatment plans.
A profound understanding of the Achilles cushion not only benefits individual athletes but also enhances our knowledge of musculoskeletal health in broader contexts.
Implications for Practice and Research
The implications of our findings extend across various fields, prompting several considerations:
- Health Benefits: Increased awareness and understanding of the Achilles cushion among healthcare providers can lead to better outcomes in preventative care and rehabilitation strategies for patients at risk.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Future studies should involve collaboration between biomechanics, physiotherapy, and sports medicine to explore innovative treatment modalities and to inform clinical practices.
- Emerging Technologies: Advances like imaging techniques could reveal deeper insights into the structural composition and functional dynamics of the Achilles cushion, guiding effective interventions.
- Educational Endeavors: Integrating knowledge about this tissue into academia can equip future practitioners with the insights necessary to prevent and treat relevant injuries effectively.



